Extending Embedded Software into FPGA Hardware
26.01.2026 Denis Vasilík
For decades, FPGA and ASIC development has lived in a world of its own. Hardware description languages like VHDL and Verilog are powerful and precise, but they come with a steep learning curve, verbose syntax, and workflows that feel disconnected from modern software engineering practices.
At the same time, embedded software developers frequently encounter the limits of MCUs and CPUs. Latency, determinism, power efficiency, and parallelism eventually become bottlenecks. While FPGAs are often the right technical answer, the barrier to entry is high enough that many teams avoid them altogether.
Livt exists to close this gap.
Livt is a general-purpose programming language for FPGA and ASIC design that brings software-style abstraction, tooling, and workflows into the hardware domain without sacrificing correctness, determinism, or interoperability with existing HDL code.
Why Another Language for FPGA Development?
Traditional HDL development forces developers to think in terms of low-level hardware concepts from the very first line of code. While this level of control is essential for correct and efficient hardware design, it also means that even simple behaviour often requires substantial boilerplate and a deep understanding of hardware-specific details.
In practice, traditional HDL development requires you to think in terms of:
- signals instead of variables
- processes instead of functions
- explicit clocks and resets throughout the design
- handwritten testbenches for verification
- vendor-specific tool flows and workflows
These concepts are powerful, but they also make FPGA development harder to approach, slower to iterate on, and more difficult to maintain - especially for developers coming from a software background.
Livt takes a different approach. Instead of starting with low-level mechanisms, you describe what a design should do, and the compiler derives a correct and readable VHDL representation from that description. The generated HDL integrates seamlessly into existing toolchains and can coexist with handwritten VHDL or Verilog whenever deeper control or optimization is required.
Livt is designed to cover what is needed for modern development:
- You describe behaviour first
- The compiler derives correct VHDL
- You retain full access to VHDL and Verilog when needed
- You work in a software-oriented ecosystem, including
- package management
- unit testing
- CI/CD integration
- AI-assisted tooling
The result is not "HDL replaced", but HDL elevated - which is also reflected in the name "Livt". The intent is not to replace hardware description languages, but to raise the abstraction level at which most of the system is expressed. Hardware engineers retain full control where it matters, while large parts of a design can be developed more quickly, more safely, and with significantly improved readability and maintainability.
Hardware-Software Integration via HxS
A key enabler of Livt's approach is its tight integration with the existing domain-specific language HxS. HxS focuses on describing hardware-software interfaces, particularly register maps and CPU-visible control points.
With Livt and HxS together, it becomes straightforward to bind a processor-accessible register to a value inside the FPGA or even to a function implemented in hardware logic. Instead of writing fragile glue logic, you define clear and explicit interfaces between software and hardware.
This fundamentally changes how processor-to-FPGA communication is designed. Hardware logic is no longer just passively controlled through registers; it can actively expose behaviour through well-defined APIs.
Why MCU Developers Should Care About FPGAs
From an MCU developer's perspective, FPGAs become relevant when software alone can no longer meet system requirements. This often happens when strict real-time behaviour is required, when latency must be reduced to an absolute minimum, or when tasks can benefit from massive parallelism.
Typical examples include high-speed sensor interfaces, motor control, protocol handling, signal preprocessing or power-efficient data processing. In many of these cases, implementing part of the functionality in hardware is the technically correct solution.
What has been missing so far is an approachable way to do this without switching entirely into an HDL-centric mindset. Livt fills this gap by offering a programming model that feels familiar to embedded developers while still producing efficient, synthesizable hardware.
A Software-Oriented Programming Model
Livt intentionally adopts concepts that are well known from modern programming languages. Code is organized using namespaces and components. State is expressed through fields. Behaviour is encapsulated in functions and processes with clear visibility rules. Constructors describe how components are wired together, rather than forcing the developer to manually manage low-level signal connections.
At the same time, the language remains explicit about what is combinational, what is sequential, and how timing is defined. This ensures that the resulting hardware remains deterministic and predictable, which is essential for FPGA and ASIC design.
This model allows mixed teams to work effectively. Embedded software developers can implement non-critical or application-specific logic, while FPGA engineers focus on architecture, timing closure, and optimization where their expertise has the most impact.
A Minimal Example: Triggering FPGA Logic via a CPU Register
A simple but representative example is a processor triggering behaviour inside the FPGA by writing to a memory-mapped register. In Livt, this boundary is expressed directly where the behaviour is defined. The following component declares a bus interface and binds a CPU-visible register bit to a function call using HxS annotations.
In this example, an AXI4-Lite bus is used. Avalon and Wishbone are supported in the same way by selecting a different bus type.
namespace Demo.App
using Livt.HxS
@Interface(BusType="AXI4Lite")
component LedController
{
led: out logic
// A write to bit 0 of this register triggers Toggle().
// Because Toggle() has no parameters and no return value,
// the compiler infers pure trigger semantics.
@Register(Id="LedToggleTrigger", Address=0x4000_0000)
public fn Toggle()
{
this.led = !this.led
}
}
At this point, it is worth noting how compact the Livt code remains. The component expresses only the essential behavior required for the task, while all bus-related infrastructure — including register decoding, address mapping, access handshaking, and protocol-compliant bus transactions - is generated automatically by the compiler and underlying framework. This avoids an entire class of bus-related errors that commonly occur when manually implementing AXI4-Lite slave interfaces.
A write to the register at address 0x4000_0000 with bit 0 set causes the function to be executed. From the compiler's perspective, this is clearly a trigger rather than a value register, because the function does not accept parameters and does not return a value.
If the function signature changes in the future, the compiler can automatically adapt the register semantics. A written value can be passed into the function, or a return value can be exposed for read-back, without changing the overall integration concept.
MCU-Side Usage (C, Memory-Mapped I/O)
From the MCU side, this looks like ordinary memory-mapped register access.
#include <stdint.h>
#define LED_TOGGLE_TRIGGER_ADDR (0x40000000u)
#define LED_TOGGLE_TRIGGER_BIT (1u << 0)
static inline void Led_Toggle(void)
{
*(volatile uint32_t*)LED_TOGGLE_TRIGGER_ADDR = LED_TOGGLE_TRIGGER_BIT;
}
int main(void)
{
while (1)
{
Led_Toggle();
// delay via timer, busy wait, or RTOS service
}
}
The firmware remains trivial, while the hardware behavior is clearly defined and close to its interface description. This tight coupling of behavior and register mapping significantly reduces integration errors and improves maintainability.
A Software-Grade Ecosystem for Hardware Design
Livt is not just a language; it is designed as a complete ecosystem. Projects follow a clear structure, support unit testing, integrate naturally into CI/CD pipelines, and benefit from AI-assisted tooling. This allows hardware projects to adopt workflows that have been standard in software development for years, improving reliability, maintainability, and development speed.
An important part of this ecosystem is the Livt base library. It provides fundamental language functionality and reusable building blocks that would otherwise need to be reimplemented repeatedly. Instead of starting from raw primitives, developers can rely on well-defined, tested abstractions that behave consistently across projects.
The following excerpt gives a small glimpse into the namespaces available when using Livt:
- Livt.Protocol Namespace
- SPI, I2C, UART masters/slaves
- AXI, Wishbone, Avalon interfaces
- Ethernet frame parsers/generators
- USB packet handlers
- Livt.Math Namespace
- Basic operations (Abs, Min, Max, Clamp, Saturate)
- Transcendental functions (Sin, Cos, Sqrt, Log, Exp, Pow)
- Fixed-point arithmetic helpers
- Bit manipulation (CountLeadingZeros, PopCount, BitReverse, RotateLeft/Right)
- Statistical functions (Average, Median, Variance, StdDev)
- Livt.Signal Namespace
- FIR/IIR filter implementations
- FFT/IFFT
- Windowing functions (Hamming, Hanning, Blackman)
- Correlation and Convolution
- CRC/Checksum calculators
This directly addresses a long-standing issue in traditional HDL-based development. VHDL suffers from fragmented and inconsistent custom package ecosystems, where every team - and often every developer - creates their own utility functions. This leads to error-prone code duplication, incompatible data type definitions across projects, and a significant long-term maintenance burden.
The lack of a comprehensive standard library beyond basic types forces engineers to repeatedly reinvent common functionality.
Livt moves away from this model. Rather than encouraging ad-hoc utility packages, it provides a coherent base library and a structured package system. On top of that, Livt encourages development at the package and framework level instead of distributing hardware as finished, opaque IP blocks with only minimal configuration options. Packages and frameworks expose structure and intent, making them easier to understand, adapt, and extend.
The following example illustrates how these building blocks come together in practice. The UartController component is composed using functionality from the Livt.Protocol namespace and exposed to a processor through an HxS register interface. Instead of integrating a finished black-box IP, the design builds on the reusable framework-level component BufferedUart and adds application-specific behaviour in a few lines of code.
namespace Demo.App
using Livt.HxS
using Livt.Protocol
@Interface(BusType="AXI4Lite")
component UartController
{
uart: BufferedUart
new (rx: in logic, tx: out logic)
{
this.uart = new BufferedUart(rx, tx)
}
@Register(Id="SayHelloWorldTrigger", Address=0x4000_0000)
public fn SayHelloWorld()
{
let greeting = "Hello, World!".Encode()
this.uart.Send(greeting)
}
}
This approach significantly reduces the learning curve for new developers, improves reuseability across teams and projects, and enables hardware development to scale in the same way modern software ecosystems do.
Not a Replacement for FPGA Engineers
Livt does not eliminate the need for FPGA engineers, nor is that its goal. Low-level optimization, timing closure, clock domain design, FSM tuning, and vendor-specific primitives still require deep hardware expertise.
What Livt does is ensure that this expertise is applied where it truly matters. Engineers spend less time on repetitive boilerplate and more time on architecture, performance, and correctness.
Closing Thoughts
Livt is about changing how FPGA and ASIC development fits into modern engineering teams. It lowers the barrier for software developers to contribute meaningful hardware logic while preserving the precision and reliability required for real hardware.
At the same time, adopting modern software concepts is becoming increasingly important to take advantage of AI-assisted programming and autonomous development agents. These tools rely on clear structure, explicit intent, and consistent abstractions — qualities that are largely absent from traditional HDL-based workflows. By embracing software-oriented design principles, Livt makes hardware designs more accessible not only to humans, but also to AI-based tooling, which is fully supported by the Livt ecosystem.
If you have ever reached a point where software alone was not enough, but hardware felt out of reach, Livt is designed precisely for that moment.
Livt is currently under active development. If you are interested in early access or collaboration, please contact us at office@eccelerators.com
Reimagining FPGA Design with AI and DSLs
20.11.2025 Denis Vasilík
At this year’s FPGA Conference 2025, we presented a new way of thinking about FPGA and ASIC design — one that combines Domain-Specific Languages (DSLs) and Artificial Intelligence to make hardware development faster, safer, and more intuitive. We explored how the growing complexity of FPGA development can be tamed by smarter tools, culminating in the introduction of Livt, our modern high-level language for FPGA and ASIC design.
The Growing Challenge of FPGA Complexity
Modern FPGAs are incredibly capable — but also increasingly difficult to work with. Today’s devices integrate millions of logic cells, heterogeneous components, and complex toolchains that often “just about work” together. Developers spend much of their time managing scripts, debugging tool compatibility, and maintaining fragile flows.
At the same time, AI models — despite their successes in software domains — still struggle to produce correct and efficient hardware descriptions. Timing, concurrency, and hardware-specific semantics remain challenging for large language models trained mostly on CPU-oriented code. Ultimately, it’s complexity that limits what developers can achieve.
Domain-Specific Languages: A Better Way to Build
To address these challenges, we are taking inspiration from decades of software evolution. Instead of relying solely on low-level languages like VHDL or Verilog, we develop Domain-Specific Languages (DSLs) — specialized programming languages designed for FPGA architectures. As illustrated below, a DSL provides an abstraction where both humans and AI can work effectively, translating high-level descriptions into detailed hardware code.
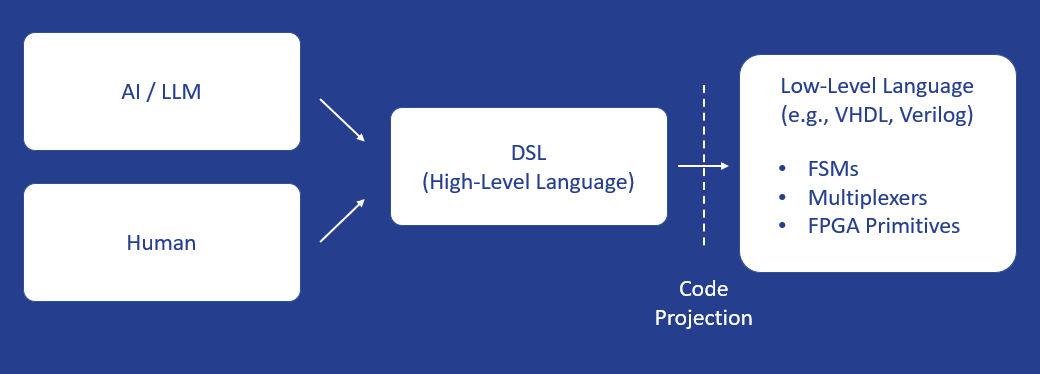
both AI and human developers to create efficient hardware designs.
In fact, we already offer HxS, a DSL for hardware–software interface design, which enables seamless communication between software components and FPGA logic. Building on this foundation, we are extending our work toward more general hardware design with Livt. DSLs focus on the core concepts of a specific problem space. They provide:
- Higher abstraction while maintaining full hardware control
- Clearer, more maintainable code
- Compatibility through compilation to VHDL or Verilog
By expressing hardware intent more directly, DSLs allow engineers to think in architectural terms rather than signal wiring and syntax quirks. This shift helps both humans and AI tools understand and reason about complex hardware systems.
Introducing Livt: A Modern Language for FPGA and ASIC Design
Livt is our answer to the complexity of FPGA development — a DSL that merges domain knowledge, modern workflows, and AI-assisted tooling. As illustrated below, Livt abstracts away low-level hardware details and moves FPGA design into the software domain, where modern development practices and AI support can unfold their full potential.
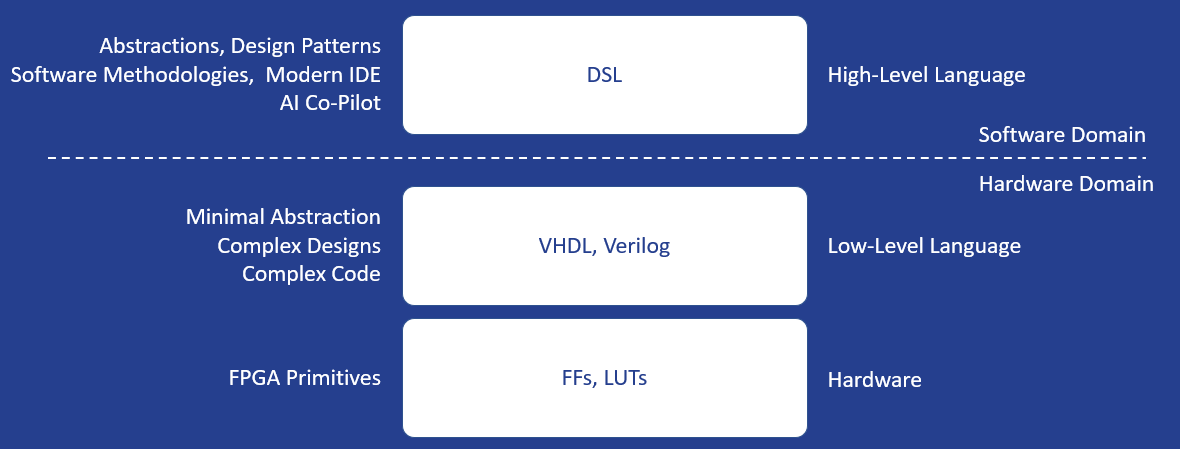
FPGA design into the software domain.
Built specifically for FPGA and ASIC projects, Livt offers:
Domain knowledge integration: Clocks, resets, FSMs, CDCs, and timing constraints are handled safely and automatically.
Error prevention: Common pitfalls in VHDL are detected early by the compiler.
Developer experience: Livt provides familiar syntax, inline documentation, and tight IDE integration.
Modern workflows: Package management, CI/CD pipelines, and vendor tool templates are included by design.
The Livt compiler acts as a quality gate, embedding expert knowledge into the language itself. Generated HDL code remains human-readable, simulatable, and synthesizable — ensuring smooth adoption for existing FPGA teams.
Livt is designed to coexist with traditional HDL flows, allowing developers to combine higher-level Livt code with detailed VHDL or Verilog implementations whenever needed. This flexibility ensures that teams can benefit from modern abstraction without losing access to low-level control where precision matters most.
Livt is currently under active development. If you are interested in early access or collaboration, please contact us at office@eccelerators.com
AI Meets DSL: Smarter Design Workflows
The true innovation comes when AI and Livt work together. Instead of replacing engineers, AI in Livt assists them — handling boilerplate code, generating tests, and providing smart auto-completion based on project context. While AI contributes language knowledge and reusable code patterns, the Livt compiler enforces hardware correctness and domain-specific constraints. This partnership results in:
- Fewer manual errors
- Faster design iterations
- Smarter, context-aware code generation
We have integrated lightweight, local LLMs (under 1.9 GB) that run directly within the IDE. Developers get immediate AI support without relying on cloud infrastructure, ensuring privacy and speed.
Turning Complexity into Capability
Our approach reflects a larger shift in engineering philosophy — transforming complexity from an obstacle into a capability. By embedding design knowledge into languages and tools, engineers can work at higher semantic levels, much like the transition from Assembler to C, and later to C++. The comparison below shows how existing languages each address only parts of the FPGA design challenge, while Livt brings all essential capabilities together into one cohesive solution.

of hardware-focused and software-oriented languages.
Our approach summarized, “To benefit from AI assistance, we must first address its challenges. That means teaching our tools — and our languages — about the domain they serve.”
This mindset turns AI from a generic assistant into a domain-aware co-pilot, supporting developers in domains where managing complexity defines success.
Looking Ahead
The combination of AI and DSLs is paving the way for a new generation of Electronic Design Automation tools — ones that understand not just syntax, but intent. With Livt, we demonstrate that higher-level languages and embedded intelligence can dramatically reduce development friction, making FPGA and ASIC design more accessible, reliable, and productive.
We continue to refine this approach, working toward the seamless integration of AI-driven development, simulation, and synthesis. The future of hardware design will not be defined by overcoming complexity — but by mastering it.
Harnessing DSLs & AI for Developer Productivity
05.03.2025 Denis Vasilík
At Eccelerators, our mission is both straightforward and ambitious: we aim to tame complexity for developers by creating EDA tools and Domain-Specific Languages (DSLs) that streamline their workflows. That’s why we conduct extensive research in AI, ensuring that these technologies genuinely serve developers rather than burdening them with additional learning curves.
Why DSLs and AI?
Many developers can confirm that DSLs, while powerful, often require a significant upfront effort to learn. However, once mastered, DSLs can drastically improve productivity and make projects more maintainable. That’s why at Eccelerators, we design, research, and refine DSLs with developer experience at the forefront. Our research covers multiple domains:
- Domain-Specific Languages (DSLs)
- Vendor Tool Integration
- Integration into Development Environments
- HxS: Our Language for Interface Design
- General-Purpose Language for FPGA/ASIC Design (in active development)
While DSLs come with a learning overhead, our goal is to minimize that cost by seamlessly integrating our languages and tools into development workflows. We leverage AI by integrating it directly into the development environment, allowing developers to climb the learning curve as they develop.
Instruction Fine-Tuning for HxS
One of our most exciting initiatives is fine-tuning an AI model specifically for HxS, our language for interface design. We employ an instruction-based approach, where we provide structured input and train the AI to generate accurate and meaningful HxS code. Here’s a simplified example to illustrate the concept:
// Create me a AXI4-Lite register interface with four registers each having 32 bits for a 32-bit databus.
As shown below, the AI-generated DSL code closely aligns with the natural language description.
// Create me a AXI4-Lite register interface with four registers each having 32 bits for a 32-bit databus.
use Eccelerators.HxS.Registers.Reg32;
namespace Eccelerators.HxS.Playground
{
interface SimpleRegisterInterface
{
Name = 'Simple Register Interface';
Description = '
This is a AXI4-Lite register interface example
with 4 registers each with a size of 32 bits.
';
AddressBusWidth = 32;
DataBusWidth = 32;
Blocks = [SimpleRegisterBlock];
BusType = BusType.AXI4Lite;
}
block SimpleRegisterBlock
{
Name = 'Simple Register Block';
Description = '
This block provides 4 R/W registers with a
size of 32 bits.
';
Registers = [
Reg32(Id="Register1"),
Reg32(Id="Register2"),
Reg32(Id="Register3"),
Reg32(Id="Register4")
];
}
}
Imagine how helpful it would be if you didn’t need to memorize every DSL statement and could simply describe what you want instead. This offers multiple benefits:
- Lowers the learning curve for developers
- Simplifies the development process
- Increases overall productivity
Higher-Level Languages for FPGA/ASIC Design
Another ongoing focus is our research into higher-level languages that can be mapped onto VHDL constructs and FPGA primitives. Traditional FPGA/ASIC design requires deep knowledge of low-level languages like VHDL. By introducing higher-level abstractions, we aim to reduce complexity and mitigate subtle errors that often arise in AI-generated code.
Early experiments indicate that these higher-level language concepts improve design correctness by eliminating common pitfalls. By encapsulating VHDL intricacies behind more intuitive constructs, developers can focus on functional requirements rather than low-level implementation details. We will delve deeper into this topic in a future blog article.
What’s Next?
At Eccelerators, our expertise in domain-specific languages and FPGA design continues to shape our work in EDA tools. We envision a future where developers can harness the power of DSLs and AI without facing steep learning curves or integration challenges.
This research is ongoing, and we are excited about our progress. Once these efforts reach a mature stage, we will integrate them into our products and make them widely available. Stay tuned for updates—we’re just getting started.
Leave the scripts behind you
07.02.2025 Denis Vasilík
When it comes to FPGA design, developers often rely on scripts to create register interfaces, documentation, and C-function stubs for software teams. While this approach may seem straightforward, it comes with significant risks and inefficiencies. Let’s explore why this traditional approach can be problematic, and how professional tools like HxS are transforming the landscape of hardware-software interface design.
The Challenge of Script-Based Workflows
Scripts are widely used in FPGA projects for generating register interfaces and the associated documentation. While convenient for small projects, this method has several drawbacks:
Error-Prone Nature: Scripts require careful attention to detail. Small errors in the scripts can lead to inconsistencies between hardware and software implementations, causing costly debugging efforts later.
Increased Effort for Updates: When changes occur—such as modifying a register interface—scripts often need significant manual rework. This ripple effect makes iterative development slower and less predictable.
Divergence Between Teams: Synchronizing updates between hardware and software teams becomes challenging, especially in larger projects where multiple stakeholders depend on accurate and up-to-date information.
The result? Wasted time, frustrated developers, and a higher likelihood of errors creeping into production systems.Why Aren’t Developers Using Professional Tools?
Given the challenges of script-based workflows, you’d think professional tools would already be the norm. However, many FPGA developers still hesitate to adopt tools like HxS. Why is that?
Perceived Complexity: Developers may assume that professional tools are harder to learn or integrate into their workflows.
Legacy Processes: Teams that have used scripts for years may be resistant to change, even if it would improve efficiency.
Lack of Awareness: Many developers aren’t aware that tools like HxS exist, or they underestimate the advantages these tools can provide.
HxS: A Proven Solution for Modern Interface Design
HxS is designed to eliminate the inefficiencies and risks of script-based workflows, offering a professional, reliable alternative for hardware-software interface design. It’s based on proven development workflows and generates everything you need—from high-quality VHDL code to comprehensive documentation and software stubs. Here’s why HxS stands out:
Error Reduction: By automating the creation of register interfaces, documentation, and C-function stubs, HxS minimizes human error. Developers can trust the generated outputs to be consistent and reliable.
Seamless Updates: When changes to the interface occur, HxS effortlessly regenerates all affected outputs. This ensures hardware and software teams stay synchronized, even in fast-paced development cycles.
High-Quality Outputs: HxS produces clean, readable VHDL code and well-documented software stubs. Teams can focus on functionality rather than debugging or deciphering code.
Proven Workflows: Built on industry-best practices, HxS integrates easily into modern development environments, including CI/CD pipelines.
Conclusion: Future-Proof Your Workflow with HxS
The days of relying on fragile scripts for interface design are over. Tools like HxS offer a smarter, more efficient approach, allowing developers to focus on innovation rather than repetitive, error-prone tasks.
By adopting HxS, FPGA teams can reduce development time, improve collaboration, and increase the overall quality of their projects. So why settle for outdated workflows? Empower your team with HxS and experience the difference in your next hardware-software interface design project.
Are you ready to elevate your workflow? Learn more about HxS here.
Automating Documentation for Hardware-Software Interfaces
10.01.2025 Denis Vasilík
In the dynamic world of embedded systems and hardware design, documentation often feels like a necessary burden. Developers understand its importance for collaboration, quality, and maintainability, yet it’s frequently an afterthought—outdated and misaligned with the project’s current state due to tight deadlines.
Automation offers a solution by transforming documentation into a seamless, accurate, and real-time process. Automating the creation of hardware-software interface documentation saves time, ensures precision, and provides a reliable resource for teams. In this blog, we’ll explore the benefits of automated documentation and the tools, like HxS, that make it possible.
Why is Documentation So Important?
In embedded systems development, the hardware-software interface acts as the bridge between two critical domains. Accurate and comprehensive documentation ensures seamless collaboration, allowing hardware and software teams to work in sync and reduce miscommunication. It minimizes errors by providing clear guidelines, preventing bugs caused by misunderstandings or incorrect assumptions. Additionally, it facilitates efficient onboarding, enabling new team members to quickly grasp the system and contribute effectively. Furthermore, it fulfills regulatory compliance requirements, ensuring safety and adherence to industry standards.
Traditional documentation methods often struggle to keep pace with the dynamic nature of development projects, presenting numerous challenges. As interfaces evolve, manually updated documents frequently fall behind, resulting in inconsistencies. The process of writing and maintaining documentation is also highly time-consuming, drawing valuable resources away from core development tasks. Additionally, tracking changes manually across teams and outputs increases the risk of human error, further complicating the process.
How Automation Transforms Documentation
Automating the documentation process addresses these challenges by ensuring it is always up-to-date. Documentation is generated directly from the source description, reflecting the current design accurately. This automation also eliminates the time spent on manual updates, allowing developers to focus on core functionality. By reducing human error, it provides consistent and reliable output. Furthermore, tools like HxS make documentation accessible by generating outputs in multiple formats, such as PDF, HTML, and Word, ensuring stakeholders receive the format they need.
Automating Documentation with HxS
HxS simplifies hardware-software interface documentation by creating a single source of truth. This central description is used to generate all necessary documentation, keeping everyone on the same page.
Real-Time Updates: Changes in the interface description are immediately reflected in the documentation.
Multi-Format Outputs: Generate consistent documentation in PDF, Word, ReStructured Text and HTML.
Style Integration: Use your existing styles and templates for professional, branded documents.
Combined Documentation: HxS supports both generated and manually created content, giving teams flexibility to add annotations or additional context.
Practical Example: A Register Interface Design
Imagine a team designing a complex register interface for an embedded system. Without HxS, they would need to manually document each register, including its behavior, fields, and access types. Every time a design change occurred, this documentation would require updates, and the team would have to share and maintain multiple document versions across teams, leading to inefficiencies and potential errors.
With HxS, the team defines the interface once in a central description. From this, HxS automatically generates detailed register specifications, field descriptions with access types, and behavioral notes accompanied by diagrams. Furthermore, when integrated into a CI pipeline, HxS ensures that documentation evolves seamlessly alongside development. Each interface update triggers automatic regeneration, enabling teams to catch discrepancies early and maintain perfect alignment between code and documentation. This integration into CI workflows streamlines collaboration and ensures the documentation always reflects the current state of the project.
Benefits Beyond Documentation
Automated documentation doesn’t just save time—it enhances your entire development workflow:
Improved Collaboration: Teams work with a unified, up-to-date reference.
Faster Iterations: Changes can be made confidently, knowing the documentation will follow.
Reduced Rework: Accurate specifications prevent costly misunderstandings.
Future-Proofing: With consistent and reusable documentation, you’re better prepared for future upgrades or redesigns.
Take the Leap Towards Automation
At Eccelerators, we believe that developers should focus on innovation, not repetitive tasks like manual documentation. With HxS, you can transform your approach to hardware-software interface documentation, making it faster, easier, and more reliable than ever.
Ready to see HxS in action? Contact us today to learn how HxS can simplify your documentation process and elevate your development workflow.
Unlocking the Power of Higher-Level Concepts in EDA
02.12.2024 Denis Vasilík
In Electronic Design Automation (EDA), traditional low-level languages like VHDL have long been the standard, offering detailed control closely aligned with hardware implementation. However, as designs grow in complexity, their limitations become apparent. To address modern demands, higher-level concepts and domain-specific languages (DSLs) provide a promising alternative. At Eccelerators GmbH, our vision is to meet these modern demands using DSLs, leveraging our expertise in creating tailored solutions for the industry.
The Challenge of Low-Level Languages
Low-level languages such as VHDL require developers to manually manage boilerplate code, register mappings, and signal propagation. As designs become more sophisticated, these manual processes result in prolonged development cycles and reduced productivity.
Higher-level concepts abstract away repetitive and intricate details, allowing developers to focus on broader functionality and design intent. In EDA, these abstractions are particularly powerful when combined with DSLs, which tailor the language to the specific needs of hardware/software interface design.
Benefits of Higher-Level Concepts
Enhanced Productivity: Higher-level concepts improve productivity by automating repetitive tasks, such as boilerplate code and register management. Tools like HxS use DSLs to centralize interface descriptions, generating necessary outputs for FPGA and software developers, as well as documentation. This automation reduces manual effort and accelerates the design process.
Improved Reusability: Reusability is key to reducing costs and ensuring consistency. Low-level approaches often produce tightly coupled code, making reuse difficult. Higher-level abstractions encourage modularity, allowing components to be reused with minimal rework. HxS generates both hardware (e.g., VHDL) and software (e.g., C/C++ headers) outputs from a single description, enhancing cross-domain applicability.
Greater Flexibility and Adaptability With low-level workflows, even minor changes can require significant rewrites. Higher-level concepts simplify modifications by centralizing design intent. DSLs like those used in HxS automatically propagate changes across all generated outputs, minimizing errors and ensuring consistency—especially valuable in agile environments.
Enhanced Collaboration: Higher-level concepts bridge gaps between diverse teams by providing a shared, comprehensible representation of the design. Low-level languages often create silos between hardware engineers, software developers, and system architects. DSLs with intuitive semantics foster collaboration by enabling all stakeholders to understand and contribute to the design process.
Challenges of Higher-Level Approaches
While the benefits are compelling, there are challenges:
Learning Curve:Teams used to low-level languages may face an initial learning curve. However, the long-term gains in productivity and reduced errors outweigh this challenge.
Loss of Granularity: Abstractions may obscure some control available with low-level languages. Tools like HxS mitigate this by generating readable, customizable low-level code.
Tool Dependency: Higher-level approaches often rely on specific tools. The success of these tools depends on their ability to integrate seamlessly into existing workflows and support industry standards.
Semantic Concepts and Developer Experience
Semantic concepts enhance the developer experience by providing clear, expressive structures that reflect design intent. This reduces cognitive load and allows developers to focus on high-level problems. Tools like HxS enforce clean and consistent register designs, ensuring that generated code and documentation are intuitive, leading to fewer errors and a smoother development process.
Higher-Level Concepts as a Competitive Edge
Higher-level concepts do more than enhance productivity—they enable innovation. By automating repetitive tasks, developers are free to explore new ideas, iterate quickly, and deliver solutions faster. In a competitive market, agility is crucial, and higher-level concepts offer a strategic advantage.
Embracing the Future of EDA
As design complexity grows, the limitations of low-level languages like VHDL become evident. Higher-level concepts, driven by semantic clarity and abstraction, pave the way for greater productivity, reusability, and collaboration. Tools like HxS exemplify the potential of higher-level approaches by leveraging DSLs and modern paradigms to empower developers. At Eccelerators GmbH, we are committed to helping our clients achieve these benefits and drive the future of EDA.
It is time for the EDA industry to embrace higher-level concepts as a strategic advantage that enables better, faster, and more flexible design processes.
HxS Release 1.0.17
03.11.2024 Denis Vasilík
Get ready to explore the latest release of HxS, version 1.0.17! Download it now and uncover a host of enhancements and bug fixes that promise an even smoother experience.
- Added Treat Warnings as Errors Compiler Flag
- Asynchronous BitBehaviour.Transparent and BitBehaviour.WriteTransparent
- Support Byte-wise Bus Access
- Fixed Overlapping Registers
- Fixed Asynchronous Bus Reset Initialization
- Fixed Parameter Syntax Validation
- Eclipse Plugin and VS Code Extension
Added Treat Warnings as Errors Compiler Flag
In this release, we have added the compiler option --treat-warnings-as-errors
or in short -t. When this option is activated, all warnings are treated as errors.
You can apply it as follows:
hxsc -t -o src-gen vhdl MyRegisterInterface.hxs
Asynchronous BitBehaviour.Transparent and BitBehaviour.WriteTransparent
As of now, it is permitted to use bit fields with BitBehaviour.Transparent or
BitBehaviour.WriteTransparent together with asynchronous registers. Notably,
even when the bit behaviour is set to transparent, the write cycle will be registered to
ensure that the data reaches its block.
register MyRegister
{
Async = true;
Bits = [MyData];
data MyData
{
BitBehaviour = BitBehaviour.Transparent;
}
}
Support Byte-wise Bus Access
Until now, accessing the bus was constrained to addresses that were multiples of 4. With this release, all three bus interfaces — Avalon, AXI4-Lite, and Wishbone — now support byte-wise bus access.
Fixed Overlapping Registers
We encountered an issue with our automatic register address calculation.
When there were, for example, three registers containing only a few bits each,
they were incorrectly assigned to the same address. In the following example,
MyRegister0, MyRegister1, and MyRegister2
would all have been assigned to address 0x0.
block MyBlock
{
Registers = [
MyRegister0,
MyRegister1,
MyRegister2
];
register MyRegister0
{
Width = 3;
}
register MyRegister1
{
Width = 9;
}
register MyRegister2
{
Width = 8;
}
}
This behavior was counter-intuitive and has been fixed. Now, registers are padded
to the next byte boundary, ensuring that each subsequent register starts at the
next available address. For example, with the registers mentioned above,
MyRegister0 starts at 0x0, MyRegister1
starts at 0x1, and MyRegister2 starts at 0x3.
Fixed Asynchronous Bus Reset Initialization
We previously missed initializing signals in the asynchronous domain, resulting in undefined signals during simulation. This issue has been addressed. Now, all signals are properly initialized and set to specific values.
Fixed Parameter Syntax Validation
There was an error in the validation process of the parameter syntax used to override properties of existing HxS objects, such as the register in the following example. This validation error prevented the overriding of properties like the Bits property, which expects lists.
block MyBlock
{
Registers = [
MyRegister(Bits=[MyData0]),
MyRegister(Bits=[MyData1])
];
register MyRegister {}
data MyData0
{
Width = 8;
}
data MyData1
{
Width = 24;
}
}
This issue has been fixed, and the parameter syntax can now be used to override lists as well.
Eclipse Plugin and VS Code Extension
With every release, we ensure the HxS Eclipse plugin and VS Code extension are up-to-date. You can find both IDE integrations ready for download here.
HxS Release 1.0.16
01.03.2024 Denis Vasilík
Great news for HxS developers: We are releasing version 1.0.16. In our ongoing commitment to security, we regularly maintain and update our dependencies. With this release, we are ensuring a robust and secure user experience. Please be aware that starting from this release, Java 17 or higher is a requirement.
In addition, we have dedicated efforts to enhance VHDL code integrity, systematically addressing syntax issues of the generated files. HxS 1.0.16 is now available in our download section.
HxS Release 1.0.15
31.01.2024 Denis Vasilík
Exciting news for HxS users: version 1.0.15 is here! This release focuses on improving VHDL code integrity, effectively fixing syntax issues across various HxS configurations. Explore these improvements — HxS 1.0.15 is now ready for you in our download section.
HxS meets Cologne Chip: Developing a CRC Calculator for GateMate FPGA
20.12.2023 Denis Vasilík
In this blog series, we will create a simple Intellectual Property (IP) core that calculates checksums, utilizing the HxS methodology for register interface description and the GateMate FPGA from Cologne Chip. Our experimental playground will be the GateMate Evaluation Board. The GateMate series brings us compact yet powerful FPGAs, perfect for a range of applications. Our focus will be on the CCGM1A1, equipped with 20,480 programmable elements, suitable for both combinatorial and sequential logic. This capacity is more than adequate for the CRC calculator we aim to create and explore in this article.
Register Interface
In this section, we dive into the world of HxS to craft a register interface. Taking inspiration from a practical example, we create a register interface for a CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) calculator, a crucial tool used in verifying the integrity of data in digital communications. We are basing our design on the same register interface as described in the ST Microelectronics reference manual (specifically, chapter 14 on page 336). It consists of the following registers:
- CRC data register (CRC_DR)
- CRC independent data register (CRC_IDR)
- CRC control register (CRC_CR)
- CRC initial value (CRC_INIT)
- CRC polynominal (CRC_POL)
Our HxS description begins with the specification of an interface. We aim for a 32-bit data bus width and an AXI4-Lite slave interface. Let's explore the HxS code that lays the foundation for our calculator:
interface CrcCalculatorIfc
{
Name = "CRC Calculator Interface";
DataBusWidth = 32;
BusType = BusType.AXI4Lite;
Blocks = [CrcCalculatorBlk];
}
Here, we define the CrcCalculatorIfc interface. It's important to note that the address bus width adapts automatically to match the actual address space used by our IP, streamlining the design process.
Next, we create a block. In HxS, blocks are instrumental in grouping registers, bringing order and clarity to complex designs. For our CRC calculator, a single block suffices to house the five essential registers, mirroring the structure found in the ST Microelectronics reference manual:
block CrcCalculatorBlk
{
Name = "CRC Calculator Block";
Registers = [
CRC_DR,
CRC_IDR,
CRC_CR,
CRC_INIT(Offset=0x10),
CRC_POL
];
}
Each register in CrcCalculatorBlk starts at a specific offset, beginning at 0x0 and increasing sequentially. Notably, CRC_INIT begins at offset 0x10, followed by CRC_POL at 0x14. HxS auto-calculates offsets and addresses, simplifying the user's workload.
Now, let's define the registers within the CrcCalculatorBlock. The CRC_DR register, a special data register, is crucial as it receives data for CRC calculation and, upon read, provides the calculated CRC. This dual functionality is efficiently handled by the ReadTransparentWriteRegisterReg32 type.
register CRC_DR : ReadTransparentWriteRegisterReg32
{
Name = "CRC Data Register";
WriteRegisterPulse = true;
}
Here, the extra write register pulse signals every new data input, triggering another CRC calculation.
The CRC_IDR is straightforward, functioning as a basic read/write register without additional complexities:
register CRC_IDR : Reg32
{
Name = "CRC Independent Data Register";
}
For controlling the CRC mechanism, we use the CRC_CR register. It enables control over various aspects of the CRC calculation:
register CRC_CR : Reg32
{
Name = "CRC Control Register";
Bits = [enum CrcControl
{
Values = [{
0 : value CrcControlReset { Width = 1; },
3 : value CrcPolySize { Width = 2; },
5 : value CrcReverseInputData { Width = 2; },
7 : value CrcReverseOutputData { Width = 1; }
}];
}];
}
CRC_INIT and CRC_POL registers provide the initial value and polynomial for the CRC calculation, respectively. The CRC_POL is set to a constant value to support the CRC-32 Ethernet polynomial 0x4C11DB7.
register CRC_INIT : Reg32
{
Name = "CRC Initial Value";
}
register CRC_POL : ReadTransparentReg32
{
Name = "CRC Polynomial";
}
With this compact yet powerful HxS description, we've laid the groundwork for a functional register interface. This approach demonstrates the ease and efficiency of prototyping with HxS. Our interface can now be iteratively refined and enriched with further details.
From this HxS description, we can generate the bus interface and comprehensive documentation in formats like Word, PDF, or HTML. Additionally, C header files facilitate embedded software integration.
Simulation
In this article, we focussed on an individual IP component rather than a complete FPGA design. Consequently, instead of creating a bitstream, we employ GHDL for simulation purposes. Our IP is simulated using the SimStm framework, a tool we developed for simulation and testing.
To begin with, we utilize the register description to generate various HxS artifacts, including the VHDL register interface and its documentation. For this process, we've set up a Linux environment, specifically using Ubuntu 22.04. The first step involves installing Ant.
sudo apt-get install ant -y
Next, we clone the actual crc-calculator repository from the Eccelerators GitHub repository:
git clone --recurse-submodules git@github.com:eccelerators/crc-calculator.git
Following that, we establish a Python3 virtual environment and install the necessary dependencies:
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
With the setup complete, we are now ready to build all the artifacts required for simulation:
make
The HxS files are located in the hxs directory. The VHDL files related to the IP and its simulation are organized within the following directory structure:
- src/vhdl This folder contains the primary VHDL source files for the IP.
- src-gen/vhdl Here, you'll find generated VHDL files specific to the AXI4-Lite interface.
- tb/vhdl This directory houses the VHDL files used for testbenching and simulation.
Additionally, the documentation for this IP, generated in various formats, is located in these folders:
- src-gen/docbook-pdf Contains the documentation in PDF format.
- src-gen/docbook-html Holds the HTML version of the documentation (Docbook).
- src-gen/html-sphinx Holds the HTML version of the documentation (Sphinx).
- src-gen/rst Stores the reStructuredText (rst) files, typically used for more textual documentation.
The simulation is executed with the following command:
make sim
A successful simulation will yield an output similar to this:
+ ./crccalculatortestbench --stop-time=100000ns
simstm/src/tb_simstm.vhd:1245:21:@@1000300ps:(assertion note): test finished with no errors!!
Next Steps
In this overview, we have outlined our process of using HxS to prototype a register description for a CRC calculator IP. We successfully created all the necessary artifacts for VHDL simulation and synthesis. As our current scope is limited to the IP component without a complete FPGA design, we focused exclusively on simulating the design. This allowed us to test and validate the IP in isolation.
In a forthcoming article, we plan to delve deeper into the specifics of how we use SimStm, our proprietary simulation framework. This exploration will provide insights into the methodologies and advantages of using SimStm for IP simulation.
Looking ahead, another article will explore the creation of a complete FPGA design for the GateMate FPGA. This will include the synthesis process and bitstream creation for the GateMate Evaluation Board. This future work aims to bring our IP from simulation to a tangible, functioning component in a real-world FPGA environment.
HxS Release 1.0.14
13.12.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are excited to unveil the newest iteration of HxS. This release brings enhancements to VHDL code's quality, addressing and fixing potential syntax errors in various HxS code configurations. Experience the improvements firsthand — HxS 1.0.14 is now available in our download section.
HxS Release 1.0.13
05.12.2023 Denis Vasilík
Get ready to explore the latest release of HxS, version 1.0.13! Download it now and uncover a host of enhancements and bug fixes that promise an even smoother experience.
- References and Scope Enhancements
- Set Default Data Bus Width to 32
- Auto-Calculation of Address Bus Width
- Derive Alignment from Data Bus Width
- Fixed Asynchronous Read-Only / Write-Only Register Bug
- Eclipse Plugin and VS Code Extension
References and Scope Enhancements
Now, you can refer to objects from the same or outer scopes without the need for their fully qualified names. When looking up a reference, the first object found is used, starting from the reference's scope and going up to the outer scope.
interface MyInterface
{
block MyBlock
{
Registers = [MyRegister];
register MyRegister {} // Hides MyRegister of outer scope
}
register MyRegister {} // Is hidden for MyBlock.Registers
}
This makes the code cleaner and more concise, as it is possible to reference objects directly without specifying their full paths each time.
Set Default Data Bus Width to 32
In this update, we have introduced a breaking change by transitioning the default data bus width from 8 to 32 bits. This modification may require adjustments in existing HxS descriptions.
interface MyInterface
{
DataBusWidth = 32; // Defaults to 32-bits and can be left out
}
Auto-Calculation of Address Bus Width
In our continuous pursuit of user comfort, we have introduced an automated
calculation for the Interface.AddressBusWidth property. Now, if no
specific value is provided, it derives the value from the blocks, eliminating
the need for manual adjustments.
interface MyInterface
{
AddressBusWidth = 8; // Is calculated and can be left out
}
Derive Alignment from Data Bus Width
The Alignment property of the Block object now determines the address alignment of contiguous registers in bytes by deriving its value from the DataBusWidth property of the associated Interface object. Given the default DataBusWidth of 32-bits, the alignment's default value is set to 4 bytes.
interface MyInterface
{
DataBusWidth = 32;
}
block MyBlock
{
Alignment = 4; // Is calculated and can be left out
Registers = [
MyRegister0,
MyRegister1,
MyRegister2
]
}
Fixed Asynchronous Read-Only / Write-Only Register Bug
Previously, defining a register as asynchronous with exclusively readable or writable bit fields could inadvertently trigger the generation of corresponding read or write parts using properties like ReadAckDelay or WriteAckDelay. This resulted in incorrect register interface behavior. We've addressed this issue, ensuring proper functionality, and now provide clear information that such properties have no effect and will be ignored.
register MyRegister
{
Async = true;
ReadAckDelay = 3;
WriteAckDelay = 3; // Ignored
Bits = [MyData];
}
data MyData
{
Width = 32;
Behaviour = BitBehaviour.Constant;
}
Eclipse Plugin and VS Code Extension
With every release, we ensure the HxS Eclipse plugin and VS Code extension are up-to-date. You can find both IDE integrations ready for download here.
HxS Release 1.0.12
31.08.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are excited to unveil HxS 1.0.12. It is now available for download. Discover a range of exciting new features such as AXI4-Lite support and improvements for IP-XACT.
- AXI4-Lite
- IP-XACT VHDL Wrapper
- Bus Reset Objects
- SPI Controller Example
- Eclipse Plugin and VS Code Extension
AXI4-Lite
After months of development and verification we added our
third bus interface AXI4-Lite. Setting the BusType
property of an interface to BusType.AXI4Lite
is enough to create an AXI4-Lite register interface.
interface MyInterface
{
BusType = BusType.AXI4Lite;
}
An AXI4-Lite HxS example can be found at the playground.
IP-XACT VHDL Wrapper
We always strive to reduce complexity and to keep tedious work
away from developers. Therefore, we introduced the vhdl.ipxact.wrapper
annotation. It instructs the VHDL generater to create a VHDL
entity without any records for use by IP-XACT. The annotation
is part of an interface object and can be used as
follows.
interface MyInterface
{
@Generator('vhdl.ipxact.wrapper', 'true')
}
Bus Reset Objects
We added the following bus reset objects to the HxS Base Library:
- BusReset.None - Bit field is not affected by bus reset
- BusReset.Sync - Bit field is affected by synchronous bus reset
- BusReset.Async - Bit field is affected by asynchronous bus reset
data MyData
{
Width = 4;
Resets = [
BusReset.None,
MySoftReset0,
MySoftReset1
];
}
The dictionary syntax can be used as well. It enhances the readability if multiple resets are defined. Here is an example:
data MyData
{
Width = 4;
Resets = {
0xU : BusReset.None,
0x5 : MySoftReset0,
0xF : MySoftReset1
};
}
Further information about the reset behaviour can be found in the documentation of the data and enum objects.
SPI Controller Example
In addition to the smaller examples at the playground, we continuously add practical examples to our the publicly available repository at GitHub. This time we added a SPI controller example, which shows advanced features of HxS.
Eclipse Plugin and VS Code Extension
We update the HxS Eclipse plugin and VS Code extension with each release. Both IDE integrations are available at the download section.
HxS Release 1.0.11
30.06.2023 Denis Vasilík
Great news! HxS 1.0.11 is now available for download. Discover a range of exciting new features and improvements.
- Added IP-XACT Extension
- Added Annotation for Identifier Customization
- Added a Playground
- Added Example Projects on GitHub
- Fixed Synchronous Registers with Asynchronous Properties
Added IP-XACT Extension
In order to improve our efforts for making HxS even more useful we added the IP-XACT extension. It can be used as follows:
hxsc -o src-gen ipxact src/MyInterface.hxs
The IP-XACT extension supports the standards spirit._1685_2009,
and accellera._1685_2014. By default, the extension generates
IP-XACT files compliant to the accellera._1685_2014 standard.
It can be changed using an annotation for the interface.
interface MyInterface
{
@Generator('ipxact.standard', 'spirit._1685_2009')
}
We are eager to improve the IP-XACT extension with each future release, so if you have any ideas how we might improve let us know.
Added Annotation for Identifier Customization
The VHDL, Python and C generators support the
{vhdl, python, c}.naming.scope annotation to
influence the creation of identifers. By default, generators
create identifiers that are unique and short in length.
Depending on the use case, it might be necessary to customize
the creation of identifers. The annotation can be used as follows:
interface MyInterface
{
@Generator('vhdl.naming.scope', 'interface')
Blocks = [MyBlock];
}
block MyBlock
{
Registers = [MyRegister];
}
register MyRegister
{
Bits = [MyData];
}
data MyData
{
Width = 8;
}
The example above will create the following identifiers for the VHDL package. The parts that are bold are influenced by the annotation.
constant MYINTERFACE_MYBLOCK_BASE_ADDRESS : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := x"00000000";
constant MYINTERFACE_MYBLOCK_SIZE : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := x"00000001";
constant MYINTERFACE_MYBLOCK_MYREGISTER_WIDTH : integer := 8;
constant MYINTERFACE_MYBLOCK_MYREGISTER_ADDRESS : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0) := std_logic_vector(x"00000000" + unsigned(MYINTERFACE_MYBLOCK_BASE_ADDRESS));
constant MYINTERFACE_MYBLOCK_MYREGISTER_MYDATA_MASK : std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) := x"FF";
Using the interface scope will create the longest
identifers, but ensures uniqueness. Further details and examples
can be found in the
documentation.
Added a Playground
In order to get to know HxS and its capabilities, we have created a playground that shows small examples of register interfaces and their corresponding HxS compiler output. The playground can be found here.
Example Projects on GitHub
In addition to our playground that provides small examples for learning purposes, we continuously work on repositories on GitHub offering practical examples.
Fixed Synchronous Registers with Asynchronous Properties
If a register has been defined as synchronous, but
has asynchronous properties like AsyncClk, AsyncRst,
ReadAckDelay or WriteAckDelay,
the generator has not ignored them. This lead to invalid VHDL
code and has been fixed in this release. In addition, a warning
is shown in case a register mixes synchronous and asynchronous
properties.
register MyRegister
{
Async = false; // Default value
AsyncClk = "MyAsyncClkSignalName"; // Is ignored, because Async = false
AsyncRst = "MyAsyncRstSignalName"; // Is ignored, because Async = false
ReadAckDelay = 3; // Is ignored, because Async = false
WriteAckDelay = 3; // Is ignored, because Async = false
}
HxS Release 1.0.10
24.05.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are happy to release HxS 1.0.10. It comes with a bunch of new features and is available at our download section.
- Added annotations for VHDL comments
- Added HxS release version to CLI
- Added VS Code content assist and documentation
Added annotations for VHDL comments
We added annotations to activate Doxygen comments for the VHDL
code generation. There are three possible options;
none, brief and detailed.
none is the default option and disables the
generation of Doxygen comments. brief adds a short
description and detailed a detailed description
to the generated VHDL code. The following example shows how to
activate Doxygen comments for the VHDL generator:
@Generator('vhdl.comments.doxygen', 'detailed')
interface MyInterface
{
Name = 'MyInterface';
Description = 'My interface description.';
Blocks = [MyBlock];
}
It is important to note that comments are only provided for the generated VHDL package. For further information about annotations, please refer to the HxS Annotations documentation.
Added HxS release version to CLI
In order to improve the version management, we added the HxS
release version in addition to the HxS compiler version to
the command line interface. It can be accessed using the
--version option.
HxS 1.0.10
HxS Compiler 1.0.16-502deb34
Copyright (C) 2023 Eccelerators GmbH
To list the versions of all installed HxS extensions, the
--extensions option can be used.
Extensions Path: /home/developer/.hxs/extensions
Extensions:
C (c) 1.0.21-830987e7
Docs (docs) 1.0.15-803f34cc
Python (python) 1.0.4-f55ac08b
simstm (simstm) 1.0.9-e0eeca02
VHDL (vhdl) 1.0.18-dc735325
Added VS Code content assist and documentation
We continuously improve the usability of HxS. In this release, we focused on the VS Code extension. The extension is now able to provide content assist and documentation for HxS objects. The latest VS Code extension is available at the Visual Studio Marketplace .
HxS Release 1.0.9
28.04.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are happy to release HxS 1.0.9. It comes with a bunch of new features and is available at our download section.
- Added CLI Error Codes to HxS Compiler
- Changed Default Behaviour for Asynchronous Registers
- Added Snake Case Support to VHDL
- Highlight Bus Reset in Eclipse
Added CLI Error Codes to HxS Compiler
In order to check error conditions of the HxS compiler, we added error codes to the CLI application. The following error codes are available:
- 0 - No error
- 1 - Unknown error
- 2 - Input file or path not found
- 3 - Invalid license file
- 4 - Unknown extension error
- 5 - Input file validation error
It is important to note that the HxS compiler always exits gracefully logging detailled error information to the log file.
Changed Default Behaviour for Asynchronous Registers
In order to simplify the usage of asynchronous registers, the
default behaviour has been changed. From now on, the
asynchronous feedback acknowledge is used as default for both
read and write acknowledge signals. This behaviour is
overriden by an external acknowledge or delay. In order to use
another acknowledge signal, the ReadExternalAck
or WriteExternalAck property has to be used. The
following example shows how to use an external acknowledge
signal and acknowledge delay instead of an asynchronous feedback:
register MyRegister
{
Async = true;
ReadExternalAck = true;
WriteAckDelay = 3;
Bits = [MyData];
}
Added Snake Case Support to VHDL
In order to support different naming conventions, the VHDL generator now supports snake case. The following example shows how to use snake case for the VHDL generator:
@Generator('vhdl.letter_case', 'snake_case')
interface MyInterface
{
DataBusWidth = 32;
AddressBusWidth = 32;
Blocks = [MyBlock];
BusType = BusType.Avalon;
}
Highlight Bus Reset in Eclipse
The first reset in a data or enum object's Resets
list determines the bus reset. In order to emphasize the special
meaning, we now highlight the bus reset in Eclipse and provide
additional information. The following examples shows a data
object with bus reset and additional reset signal:
data MyData
{
Resets = [
MyBusReset,
MyAdditionalReset
];
}
HxS Release 1.0.8
31.03.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are happy to release HxS 1.0.8. It comes with a bunch of new features and is available at our download section.
Added Avalon Bus Interface
It is now possible to switch between Wishbone and Avalon bus
interfaces. Therefore, we added a new property named BusType
to the interface object. Setting BusType.Avalon
will create a bus interface for Avalon as can be seen below.
namespace MyNamespace
{
interface MyInterface
{
BusType = BusType.Avalon;
}
}
The following entity will be created providing AvalonDown
and AvalonUp records for the bus connection.
entity MyInterfaceAvalon is
port (
Clk : in std_logic;
Rst : in std_logic;
AvalonDown : in T_MyInterfaceAvalonDown;
AvalonUp : out T_MyInterfaceAvalonUp;
Trace : out T_MyInterfaceTrace; -- optional
Selects : in T_MyInterfaceSelects; -- optional
MyInterfaceBlockDown : out T_MyInterfaceBlockDown; -- optional
MyInterfaceBlockUp : out T_MyInterfaceBlockUp -- optional
);
end;
Have a look at the Interface section of our documentation for further information.
Added Python Extension
In addition to the C extension we added a Python extension that generates variables for addresses, offsets, sizes and masks making the code more readable and enhancing the productivity of Python users.
~$ hxsc -o src-gen-python python src/MyInterface.hxs
Added --format / -f option to HxS Compiler CLI
In addition to use the auto-formatter of our IDE plugins it
is now possible to use the hxsc CLI tool to format
HxS files. This is especially useful for CI / CD pipelines
or pre-commit hooks in order to enforce auto-formatting of
HxS files.
~$ hxsc --format src/MyInterface.hxs
HxS Release 1.0.7
03.03.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are happy to release HxS 1.0.7. It comes with a bunch of new features and is available at our download section.
- Added external Acknowledge Signals
- Added Feedback for Asynchronous Acknowledge
- Added Content Assist to HxS Extension for VS Code
- Fixed Multi-File References of HxS Plugin for Eclipse
Added external Acknowledge Signals
Registers can now have external acknowledge signals for read or write accesses. They are enabled using the ReadExternalAck or WriteExternalAck properties. Further information is available in our documentation of Registers.
namespace MyNamespace
{
register MyRegister
{
ReadExternalAck = true;
WriteExternalAck = true;
}
}
Added Feedback for Asynchronous Acknowledge
It is now possible to specify whether to feedback the acknowledge signal for asynchronous read or write accesses.
namespace MyNamespace
{
@Generator('vhdl.use_async_read_ack_feedback', 'true')
@Generator('vhdl.use_async_write_ack_feedback', 'true')
register MyRegister
{
ReadExternalAck = true;
WriteExternalAck = true;
}
}
Added Content Assist to HxS Extension for VS Code
We continuously improve the HxS extension for VS Code. This time we implemented the content assist feature, so that properties of HxS objects are shown in the editor.
Fixed Multi-File References of HxS Plugin for Eclipse
We fixed a bug were the HxS plugin for Eclipse was unable to resolve references to HxS objects located in different files.
HxS Release 1.0.6
24.02.2023 Denis Vasilík
We are proud to release HxS 1.0.6. It comes with a bunch of new features and is available at our download section.
- Changed Wishbone bus interface signal and type names
- Added support for Block, Register and Delegate selects
- Added a bus monitor for VHDL bus interfaces
- Added a configuration file for the HxS compiler
- Improved error handling of the HxS compiler
Bus Interface Signal and Type Names
We strive at continuous improvement and therefore we updated the signal and type names of the Wishbone bus interface. It is now concise, easily readable and consists of exactly the information needed. Please note that this is a breaking change and existing consumers of the Wishbone bus interface must be updated.
entity ExampleWishbone is
port (
Clk : in std_logic;
Rst : in std_logic;
WishboneDown : in T_ExampleWishboneDown;
WishboneUp : out T_ExampleWishboneUp;
Trace : out T_ExampleTrace; -- optional
Selects : in T_ExampleSelects; -- optional
ExampleBlockDown : out T_ExampleBlockDown; -- optional
ExampleBlockUp : out T_ExampleBlockUp -- optional
);
end;
Block, Register and Delegate Selects
Block, register and delegate selects have been added to provide additional signals for bus access multiplexing. Detailed information is available in our documentation of Blocks, Registers and Delegates.
block MyBlock
{
Selects = [MySelect];
}
register MyRegister
{
Selects = [MySelect];
}
delegate MyDelegate
{
Selects = [MySelect];
}
select MySelect
{
Behaviour = SelectBehaviour.ReadWrite;
}
Bus Monitor
The task of the bus monitor is to prevent any blocking of the bus. In addition, it provides diagnostics about bus usage behaviour such as illegal addresses or access timeouts. Diagnostic information can be accessed using the Trace record provided by the bus interface.
entity ExampleWishbone is
port (
Clk : in std_logic;
Rst : in std_logic;
WishboneDown : in T_ExampleWishboneDown;
WishboneUp : out T_ExampleWishboneUp;
Trace : out T_ExampleTrace;
Selects : in T_ExampleSelects;
ExampleBlockDown : out T_ExampleBlockDown;
ExampleBlockUp : out T_ExampleBlockUp
);
end;
Configuration File
The HxS compiler uses now a configuration file in order to specify settings of HxS generators. The file is named hxsc.properties and is located in the HxS installation directory. The --config compiler argument shows a list of available configuration settings. It is notable that the list of configurations depend on HxS compiler extensions installed.
~$ hxsc --config
# Configuration path: /home/eccelerators/.hxs/hxsc.properties
c.api.url=https://api.eccelerators.com
docs.api.url=https://api.eccelerators.com
simstm.api.url=https://api.eccelerators.com
vhdl.api.url=https://api.eccelerators.com
Improved Error Handling
The HxS compiler now handles internal errors more gracefully without dumping stack traces to the console. Detailed error information is written into a log file that is located in the installation directory at logs/hxsc.log.
